ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Background. Epilepsy poses a prominent social and economic burden on both patients and society as a whole. The importance of the psychosocial effects of epilepsy has been increasingly recognized that accounts for a need to quantify the quality of life (QoL) of such patients to reveal areas requiring improvement and to justify a reason to invest in social safety net programs.
Objective: To identify factors associated with QoL of patients with epilepsy, analyze an impact of QoL on direct medical costs to support health policy and financing decision-making processes.
Material and methods. The total of 384 adult patients participated in the study, each of them filled in the Russified QOLIE-9 version. The influence of different factors on QoL, and QoL on direct epilepsy-related medical expenses determined on the basis of the results of copying outpatient records, was evaluated. Correlation and regression analysis methods were applied to assess study data.
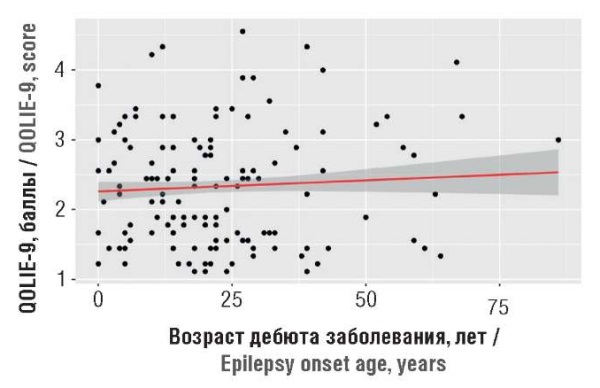
Results. Correlation analysis demonstrated statistically significant (p<0.05) factors affecting QoL such as place of observation, patient's age, length of history, presence of disability group, education level, labor status, etiology of the disease, seizure type and frequency. While assessing an association between the amount of direct medical expenses and QOLIE-9 results, a moderately close direct relationship was established.
Conclusion. QoL of patients with epilepsy declines with age, and the costs related to the disease increase regardless of the disease onset age. Comorbid, metabolic and structural etiologies of the disease, illiteracy, unemployment, hospital stay and generalized seizure type are significantly associated with lower QoL. Future research should focus on a comprehensively assessed QoL of patients with epilepsy, including medical and social aspects to develop and implement effective programs aimed at reducing stigma and improving access to medical and medication care.
Background. In 2019, a multidisciplinary scientific and clinical project Falling Patient unparalleled worldwide was launched in Russia by the Association of Epileptologists and Patients. The goal of the project is to build up a database investigating an issue of falls in medicine to reduce injury incidence and improve the quality of patients’ lives in accordance with the risk-based model of medicine in Russia. Regular Falling Patient conferences for healthcare professionals are held, featuring lectures and presentations covering a wide range of diseases and conditions related to falls and injuries, including neurological, mental, endocrinological, cardiological and other disorders. Differentiated approaches to diagnosis, prevention, treatment and rehabilitation are highlighted.
Objective: To investigate how scientific and practical information presented at the Falling Patient conferences influences clinical practice of healthcare specialists and contributes to their professional development, as well as how physicians applied the knowledge gained from these conferences in their daily clinical practice and scientific work.
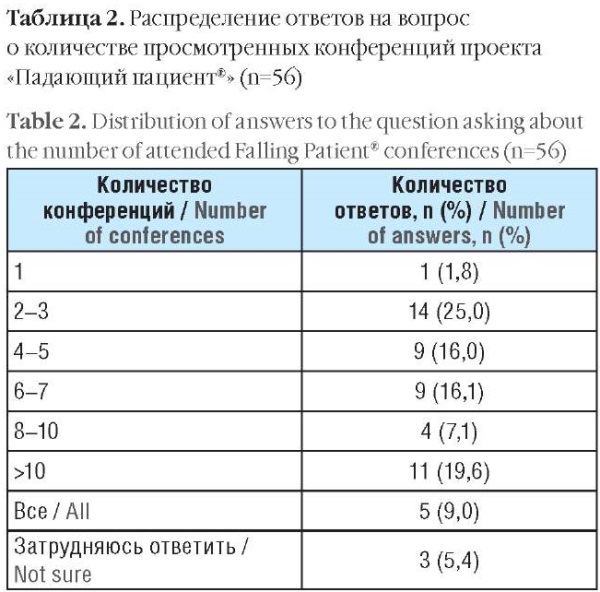
Material and methods. In our online survey, 56 physicians of various specialties from 35 cities and towns across Russia participated, all of whom had attended the project's conferences between 2019 and 2025. The questionnaire contained items asking about the respondents’ experience and insights they learned from the conferences and how they implemented this knowledge in personal clinical practice. The responses were categorized into groups: main topics, areas of focus, effects.
Results. The participants reported about mastering new approaches and algorithms for differential diagnosis of diseases, gaining an understanding regarding the multifactorial nature behind falls, acquiring knowledge on modern evidence-based therapeutic tools and rehabilitation methods for neurological disorders. Such insights allowed physicians to improve patient routing, heightened clinical awareness that positively influenced healthcare quality.
Conclusion. The Falling Patient project effectively integrates clinical and practical knowledge and experience, ensuring continuity in medical education and promoting professional development among healthcare specialists in Russia.
Background. Women of reproductive age account for 40% of all patients suffering from epilepsy in Russia. Epilepsy course varies during pregnancy as follows: full control (up to 66%) is achieved in most cases; alternatively, incidence of epileptic episodes remains unaltered, but disease course may deteriorate in as high as 15.8% cases. The current study was conducted within the framework of creating the Russian Register of Pregnancy and Epilepsy.
Objective: Analysis of epidemiological indicators of epilepsy and epileptic syndromes among pregnant women in the Smolensk Region.
Material and methods. Medical documentations of pregnant, parturient and puerperant women examined by a neurologist due to generalized and partial seizures in the anamnesis or occurring in ongoing pregnancy in the years 2019 and 2024 were retrospectively analyzed at the Perinatal Center of the Multidisciplinary Hospital of the Clinical Hospital No. 1 (Smolensk). Epilepsy epidemiology and pattern in pregnant women in the Smolensk Region were studied by assessing and discussing received medications, delivered obstetric care, as well as fetal congenital malformations.
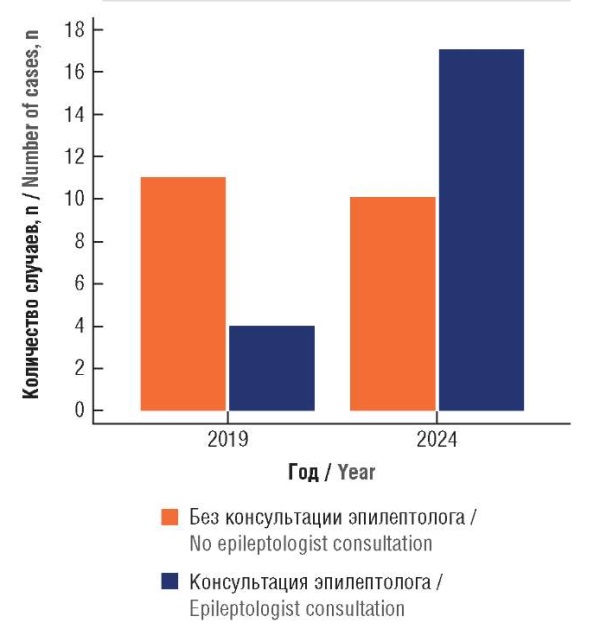
Results. The total number of pregnant patients with a history of epilepsy and epilepsy syndrome comprised 28 in 2019 (7.35% of all neurological pathology cases), and 28 in 2024 (6.41%). The study demonstrated type-specific epilepsy pattern including generalized epilepsy (71.4% in 2019, 68.2% in 2024), partial epilepsy (28.6% in 2019, 31.8% in 2024). In addition, anti-epileptic therapy was assessed showing significantly increased percentage of lamotrigine use in 2024 compared to 2019 (р=0,0086). The decline in prevalence of valproic acid use in 2024 vs 2019 was insignificant (р=0,26), with the existing experience of congenital fetal malformations. The choice of delivery tactics in patients with epilepsy was in favor of Caesarean section.
Conclusion. The results suggest a need for further retro- and prospective analysis to improve managing pregnant and parturient women with epilepsy.
SCIENTIFIC SURVEYS
This article investigates the phenomenon of epileptic aura in the context of medicine and literature. An epileptic aura is a focal epileptic seizure that occurs without loss of consciousness and manifests with visual, auditory, olfactory, tactile and other hallucinations. The descriptions of epileptic auras in the literature works of outstanding writers such as M.A. Bulgakov, F.M. Dostoevsky and L. Carroll are presented. The description of this epilepsy-related manifestation complements the psychological and physical experiences described in the works. The article combines scientific approach to studying epileptic auras and literary analysis, thereby emphasizing its relevance and informative impact for both the medical and literary community.
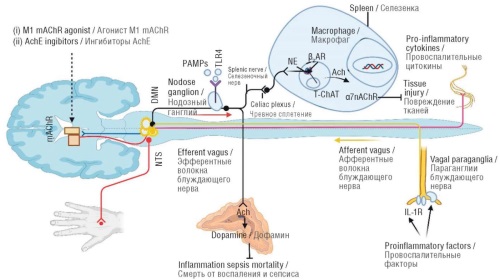
Bioelectronic medicine is a field of study that is constantly evolving as a result of recent advancements and improvements in bioelectronic technology, which have led to novel approaches and perspectives in disease diagnosis and therapy, particularly in the inflammatory reflex immuno-regulatory functioning and, vagus nerve stimulation (VNS). The vagus nerve, an elongated nerve in the autonomic nervous system, controls a number of physiological processes in humans, including blood pressure, breathing rate, vasomotor activity, and certain reflex movements. Recent bioelectronic research has led to clinical tests using VNS for inflammatory diseases and other conditions. By sending steady, gentle electric impulses through the vagus nerve to the brain, bioelectronic devices can activate the vagus nerve. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with bioelectronic medicine is transforming drug development processes. AI technology can accelerate or even eliminate many time-consuming tasks, allowing healthcare professionals to use their time more efficiently and ultimately improving healthcare outcomes. This review discusses the vagus nerve’s roles in inflammation, stimulation, and regulation in animal models, as well as its therapeutic potential in treating human inflammation. Additionally, it examines how AI-powered bioelectronic drugs are being explored for conditions such as paralysis and immune disorders, and addresses the challenges of delivering large molecules using these drugs. The article emphasizes current trends, advancements, and the promising future applications of combining AI with bioelectronic medicine.
Phantom is a false sensation, an illusion of the presence of a lost body part. A distinction is made between phantom sensations (painless phantom), phantom pain and amputation pain. Soon after amputation, up to 98% of patients experience sensations in the lost body part: they feel warmth or cold, itching, pressure and even feel position of the phantom limb in space. Often, such sensations are accompanied by excruciating pain, significantly reducing the quality of patients’ life. Since the beginning of the 16th century, descriptions of phantom pains have been recorded based on the stories of people with amputated limbs or from the retellings of doctors that caused skeptical disbelief in some specialists. The review presents descriptions of phantom limbs in autobiographical and fiction literature and analyzes them.
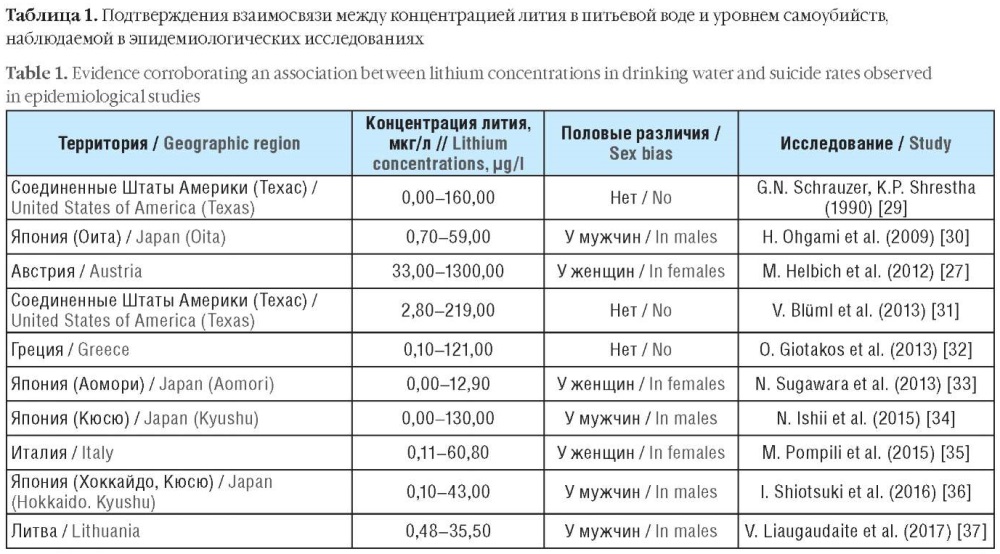
Studies conducted over the past 40 years point at the essentiality (vital necessity) of the ultramicroelement lithium. One of the microelement essentiality criteria relies on available clinical and epidemiological studies corroborating the negative consequences of insufficient lithium consumption on a population scale. Sufficient lithium supply exerts a neuroprotective, nootropic and normothymic effect. Lower blood lithium levels are associated with an increased risk of developing varicose veins, sleep disorders, extrapyramidal disorders and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Extensive clinical and epidemiological data base demonstrates a clear relationship between lower lithium-ion levels in drinking water and an increased risk of suicide, psychotic stress disorders, addiction diseases, serious crime and impulsive behavior (which is a risk factor for both suicidality and aggression leading to serious crimes). Taking lithium preparations helps to slow down dementia (both vascular and neurodegenerative forms) and other behavioral aging-associated disorders, including a total risk of tumor diseases, fractures, overeating and bulimia. The use of lithium salt-based preparations and better lithium supply through drinking water can lower seizure readiness, impulsive behavior, risk of suicide, anxiety and depression in patients with epilepsy. The current article presents the results of scientific literature systematization on this issue.
EEG РRACTICAL AND TECHNICAL ASPECTS
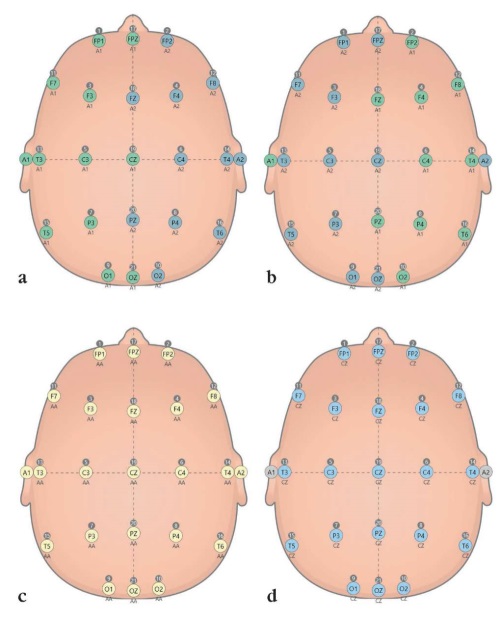
The reference electrode is an integral part in each electroencephalographic (EEG) derivation involved in recording montage. In the era of ink-writing EEG devices, contact between the active and reference EEG electrodes was established manually using special switches. Now, with the advent of computer electroencephalographs, EEG leads are formed not only at the hardware level, but also at the software level. Several types of reference electrodes have emerged: ear, central, averaged, combined ear, Laplace reference, etc. It is not surprising to get confused in such abundance. This publication details a role for active and passive (reference) electrodes, introduce the concept of EEG derivation, recording montage as well as dissects the differences between hardware and software reference electrodes. A proper understanding of how EEG equipment operates at the level of active and reference electrodes may help medical personnel in its correct set up and interpreting EEG examinations data.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
ISSN 2311-4088 (Online)