ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Background. The International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) has provided recommendations on the terminology of medicines for control of seizure disorders, which should be adapted into different languages.
Objective: to evaluate the usage profile of terms describing the effects of medicines used in patients with epilepsy.
Material and methods. The search query analysis systems Google Trends and Yandex Wordstat as well as PubMed/MEDLINE, Google Scholar and eLibrary databases were used to evaluate the general public and professional usage profile, respectively.
The following terms in Russian and English were studied: “antiepileptic”, “antiepileptic drug”, “antiseizure”, “antiseizure drug”. In order to ascertain a prevailing opinion within professional and patient communities, a questionnaire survey was conducted on the public online resources of the non-profit partnership “The Association of Epileptologists and Patients” carried out via the cloud-based cross-platform social media as well as instant messaging service Telegram and the social media platform VK.
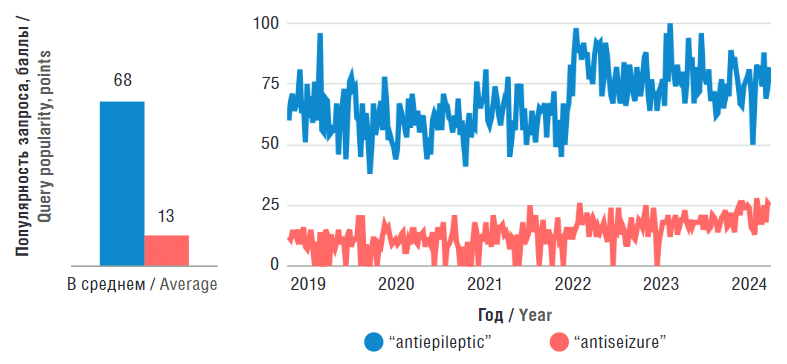
Results. In the English-speaking internet segment, the term “antiepileptic” is used more than 5 times frequently than “antiseizure” by the general public. Conversely, in the Russian-language segment, the term “antiseizure” is almost 2.5 times more common. The term “antiepileptic” is more prevalent in scientific community in both segments. This finding aligns with the profile of terminology usage observed among epileptologists and epilepsy patients. The questionnaire survey results revealed that 56.42% of 179 respondents were in favor of the terms “antiepileptic drug”, “AED” and “antiepileptic therapy”, whereas as few as 17.32% of those endorsed the ILAE-proposed terminology.
Conclusion. In light of the established practice of terminology use in both professional scientific community and among practicing epileptologists and epileptic patients, as well as the differences in the semantics of English- and Russian-language terms and the identified lack of precision in the ILAE definition of epilepsy, it can be concluded that for the Russian-speaking population, the terms “antiepileptic drug”, “AED” are more preferable rather than the terms “antiseizure medication”, “ASM”. Additionally, it is preferable to use the terms “convulsive ictus” and “epileptic ictus” due to negative connotation with term “seizure” in Russian. The terms “antiseizure” and “antiepileptic” should not be regarded as mutually exclusive in the context of treatment that has a direct impact on epilepsy course. Finally, it is necessary to further refine epilepsy definition and classification.
Background. Despite a wide range of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) with an improved pharmacological profile, patients often experience a variety of side effects during long-trem anticonvulsant therapy, among which are osteoporotic disorders. Currently, the mechanisms of AED effect on bone metabolism remain poorly understood, which creates certain difficulties in prevention and treatment of AED-induced osteoporosis.
Objective: to study bone mineral density and laboratory parameters of bone metabolism in patients with epilepsy and longterm AED administration.
Material and methods. A cross-sectional study included two comparison groups: 100 adult patients with epilepsy receiving AEDs for more than 12 months and 58 healthy volunteers without taking AEDs. All participants underwent general clinical examination, computed tomography (CT) densitometry at three time points (L1, L2 and femoral neck) and laboratory tests of mineral metabolism.
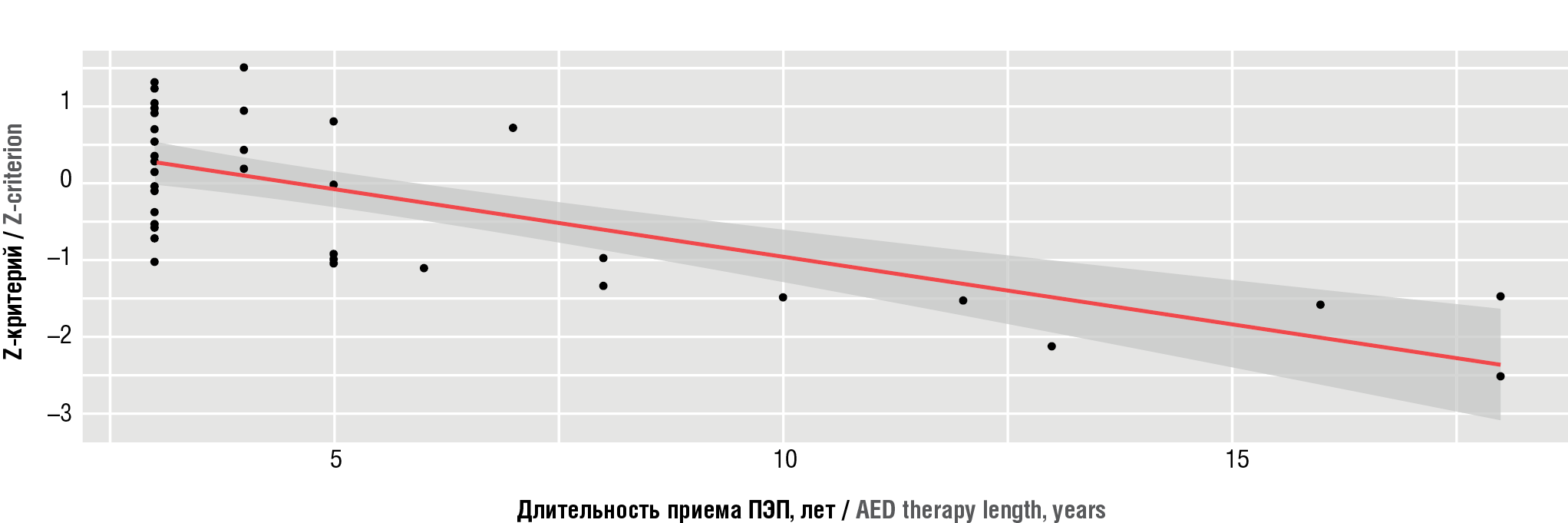
Results. According to CT-densitometry results, a decrease in bone mineral density was detected in the majority of participants from both study groups. While assessing an impact of osteoporosis risk factors on bone tissue in epileptic patients, low motor activity and duration of AED therapy were the most significant, which was associated with lower bone mineral density indices. The study of laboratory mineral metabolism indicators revealed significant inter-group differences in indicators such as ionized calcium, 25-hydroxy-calciferol, free thyroxine and prolactin (p(U)=0.044, p(U)=0.040, p(U)=0.001, p(U)=0.003, respectively).
Conclusion. The intermediate study results showed that long-term anticonvulsant use negatively affected bone metabolism in patients suffering from epilepsy. The data obtained point at need for further in-depth study of AED therapy effect on mineral metabolism.
Objective: to evaluate the results of surgical treatment and identify related predictors of unfavorable outcome in patients with temporal drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE) in long-term postoperative period.
Material and methods. Fifty-one patients with temporal lobe DRE were examined using clinical, neuroimaging, electro- physiological, and laboratory research methods from June 2020 to June 2023. Anteromedial temporal lobectomy (AMLE) and selective amygdalohippocampectomy (SAHE) were performed in 38 (74.5%) and 13 (25.5%) cases, respectively. Postsurgery outcomes were evaluated in 51 patients 6 months later, continued in 43 and 20 patients 1 year and 2 years, respectively, afterwards.
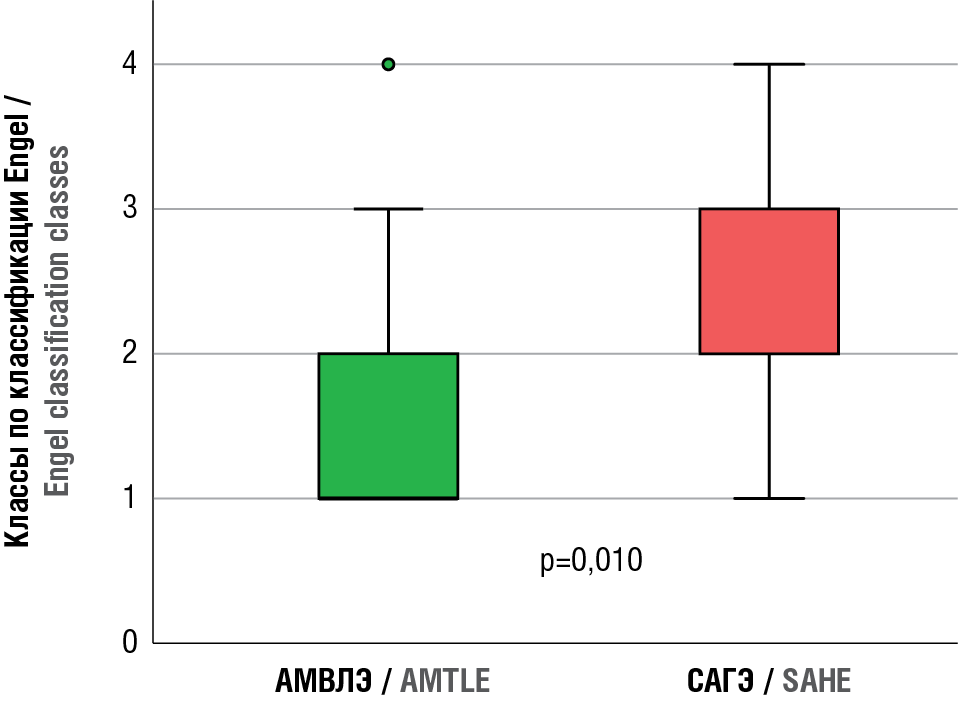
Results. The percentage of patients with significant improvement (Engel I/II) 6 months, 1 year and 2 years post-surgery was 82.4%, 72.1%, and 55.0%, respectively. After AMLE vs. SAHE, patients had a more favorable outcome while assessing seizure control. The predictors of unfavorable post-surgery outcome included a prolonged epilepsy course before surgery, the presence of electroencephalography-verified epileptiform activity in postoperative period, and repeated surgical intervention. Patient age, the presence of focal seizures evolving into bilateral tonic-clonic seizures as well as more frequent seizures before surgery were considered as potential predictors.
Conclusion. The study results show that quite high effectiveness of seizure control in postoperative period in temporal DRE is quite high that may be accounted for by probability of removing epileptogenic foci and suppression of the mechanisms ensuring emergence and irritation of epileptic discharges. Nevertheless, effectiveness of surgical treatment fades off with time, which requires to further investigate the negative factors countering long-term post-surgery effect. In connection with this, a special attention should be paid to factors such as the presence of electroencephalography-verified epileptiform activity in postoperative period, repeated surgical intervention as well as prolonged epilepsy before surgery.
Background. Epilepsy underdiagnosis in Russia, population aging, innovative drugs and expensive treatment regimens, the introduction of additional and alternative methods such as neurosurgery, annually increase the cost for treatment of epilepsy patients. In this regard, an issue of maximizing benefits for the largest number of the population becomes relevant. Pharmacoeconomical research within the assessment of healthcare technologies helps to choose the most economically and medically effective treatment strategy among numerous alternatives.
Objective: analysis of epilepsy-associated costs in the Russian Federation, aimed at supporting decision-making processes in the field of health policy and financing.
Material and methods. The empirical study was based on collecting the data on a continuous sampling of 384 epilepsy outpatient records from subjects aged 19 to 79 years for the period 2019–2022. The issues related to all costs of epilepsy were discussed. While planning, conducting and analyzing these studies, the principles of strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) were taken into account.
Results. The total annual per-patient expenditure on epilepsy treatment comprised a fifth of gross domestic product per capita. Indirect costs exceed direct cost savings. It was found out that the economic damage caused to society, family, and individual related to epilepsy is three times higher than the direct costs.
Conclusion. The results obtained are consistent with other publications in which unemployment among epilepsy patients is one of the major cost-determining factors and illustrates a critical need to maintain employment for such patients or to find suitable alternative work through professional retraining.
CASE STUDIES
Two cases of epilepsy in patients with a rare hereditary pathology associated with a chromosomal mutation caused deletion of chromosome 14 are presented. In the first case, this pathology was manifested in the child by generalized tonic-clonic seizures, delayed psycho-verbal development, and facial skull microanomaly. In the second case, it was expressed in tonic epileptic seizures, delayed psycho-verbal development, developmental microanomalies, pyramidal atactic syndrome and hand joint hypermobility. Such clinical observations are of professional and scientific interest, as they relate to a rare neurological pathology, with drug-resistant epilepsy as a leading sign.
SCIENTIFIC SURVEYS
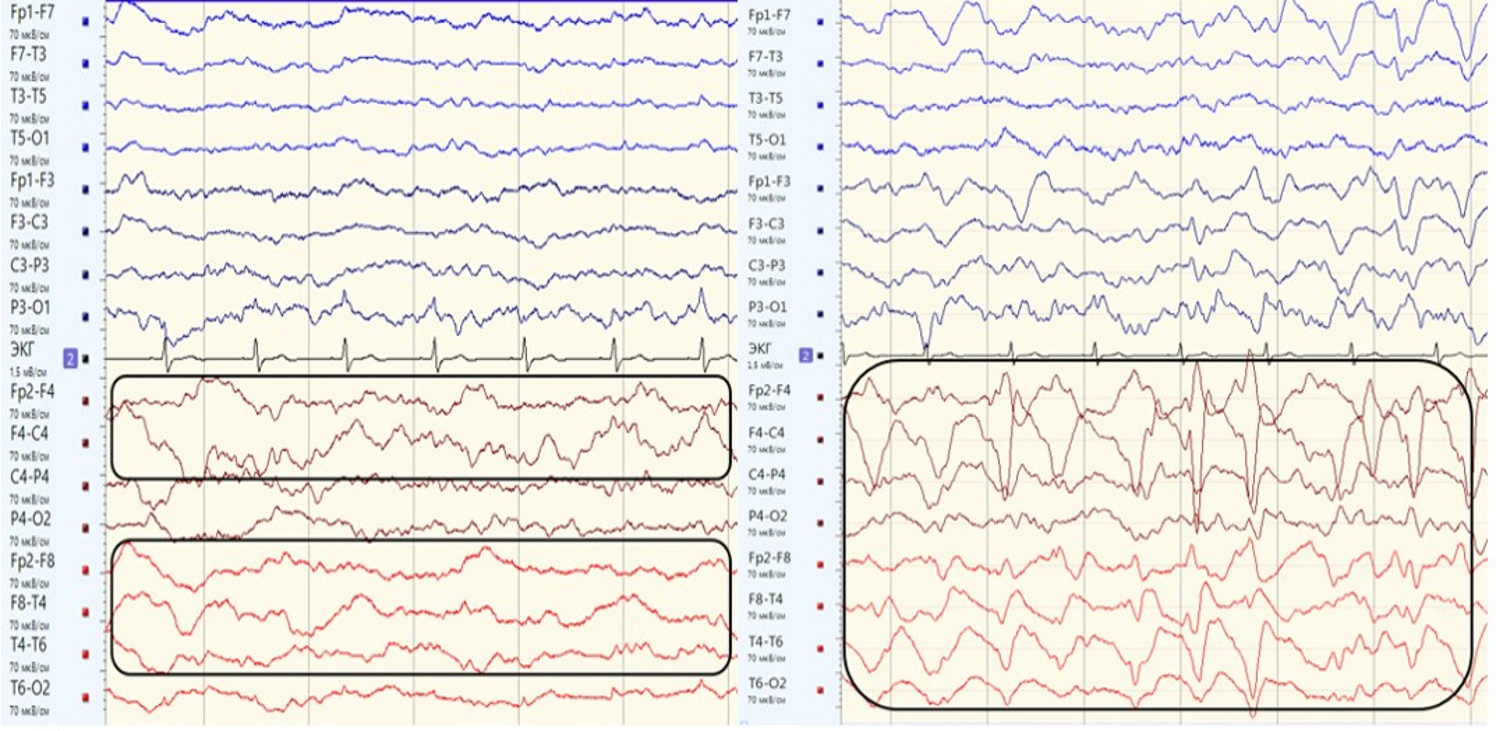
Intensive care of patients with acute non-traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage primarily relies on diagnostics of delayed cerebral ischemia (DCI). The major difficulty in detecting DCI emerges upon suppression of wakefulness, when clinical assessment of growing neurological deficit becomes complicated. Widely used transcranial dopplerography allows solely to verify a vasospasm development not always leading to DCI exhibiting a multifactorial underlying mechanism. Electroencephalography (EEG) is the only broadly available instrumental tool ensuring a continuous monitoring of cerebral functional status including in subjects at intensive care unit. To date, non-specific EEG parameters pointing at development of acute cerebral injury were identified that provide varying diagnostic and predictive informative value in DCI. We reviewed publications aimed at assessing the data on visual and quantitative EEG parameters such as regional slowing, alpha rhythm spectral power and relative variability, alpha-to-delta power ratio, and detection of epileptiform activity. Having searched international and Russia-wide medical databases, we found only 7 publications quantitatively assessing diagnostic value of EEG monitoring, which showed that for DCI diagnosis its sensitivity ranged from 76% to 100%, and specificity – from 54% to 100%. We also present a clinical case with a 70-year-old female patient who underwent surgery for non-traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage due to a ruptured aneurysm of the communicating segment of the right internal carotid artery. During the continuous videoEEG monitoring 2 days before clinical deterioration and appearance of ischemic changes in the right cerebral hemisphere on computed tomography scans, an ictal-interictal continuum pattern was noted to emerge. Future studies should be aimed at clarifying and validating the most informative DCI biomarkers including while recording EEG with intracranial electrodes that may contribute to development of automated algorithms for DCI detection.
Cortical developmental malformations (CDM) include a large group of heterogeneous brain formation disorders occurring in prenatal period. Current classifications comprise the underlying processes in CDM genesis. The article provides recent conceptions about CDM types such as gray-matter heterotopia and focal cortical dysplasia, which commonly cause epilepsy, often resistant to drug therapy. Rapid advances in improving neuroimaging techniques and molecular genetics in recent years have substantially increased the number of recognized CDM forms.
Background. According to the World Health Organization, about 50 million people worldwide suffer from epilepsy. Almost 1/3 of patients are diagnosed with drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE). A relationship between intestinal microbiome (IM) and the central nervous system carried out throughout life via bidirectional dynamic network exists. It has been evidenced that IM profile becomes altered in patients with DRE.
Objective: to summarize the current literature data on the role for microbiome-gut-brain axis in DRE, as well as to assess an importance of IM composition changes as a prognostic marker for developing DRE.
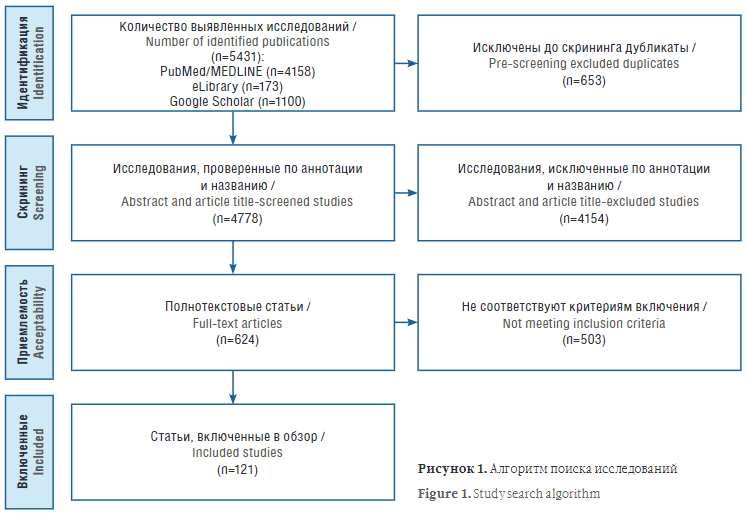
Material and methods. The authors conducted a search for publications in the electronic databases PubMed/MEDLINE and eLibrary, as well as Google Scholar search engine. The evaluation of the articles was carried out in accordance with the PRISMA recommendations. Based on the search, 4,158 publications were retrieved from PubMed/MEDLINE database, 173 – from eLibrary, and 1,100 publications found with Google Scholar. After the selection procedure, 121 studies were included in the review.
Results. The review provides convincing evidence about a correlation between IM and DRE demonstrating overt differences in IM composition found in patients with epilepsy related to drug sensitivity. IM dysbiosis can be corrected by exogenous interventions such as ketogenic diet, probiotic treatment and fecal microbiota transplantation subsequently resulting in altered brain neurochemical signaling and, therefore, alleviating epileptic activity.
Conclusion. A ketogenic diet, probiotics and antibiotics may have some potential to affect epilepsy by correcting IM dysbiosis, but the current studies provide no proper level of evidence. Future clinical multicenter trials should use standardized protocols and a larger-scale patient sample to provide more reliable evidence. Moreover, further fundamental investigations are required to elucidate potential mechanisms and therapeutic targets.
Objective: to systematize scientific data on biomedical studies investigating trace element lithium over the past 70 years; evaluate toxic properties of lithium ascorbate (LiAsc) as an important promising candidate molecule.
Material and methods. An analysis of 49,959 publications on lithium biomedical research retrieved from PubMed/MEDLINE database was carried out using modern data mining methods developed within the framework of topological approach to recognizing (Yu.I. Zhuravlev scientific school). Publications found by experts and not indexed in PubMed/MEDLINE were used in discussing the results of a systematic analysis of publications array retrieved from PubMed/MEDLINE. An experimental study of chronic 180 day-long LiAsc (at doses of 5, 50 and 150 mg/kg) toxicity was performed on 36 “Soviet chinchilla” rabbits by assessing local irritant action. Intoxication clinical picture, body weight dynamics, water and food intake as well as physiological, hematological and biochemical parameters were analyzed.
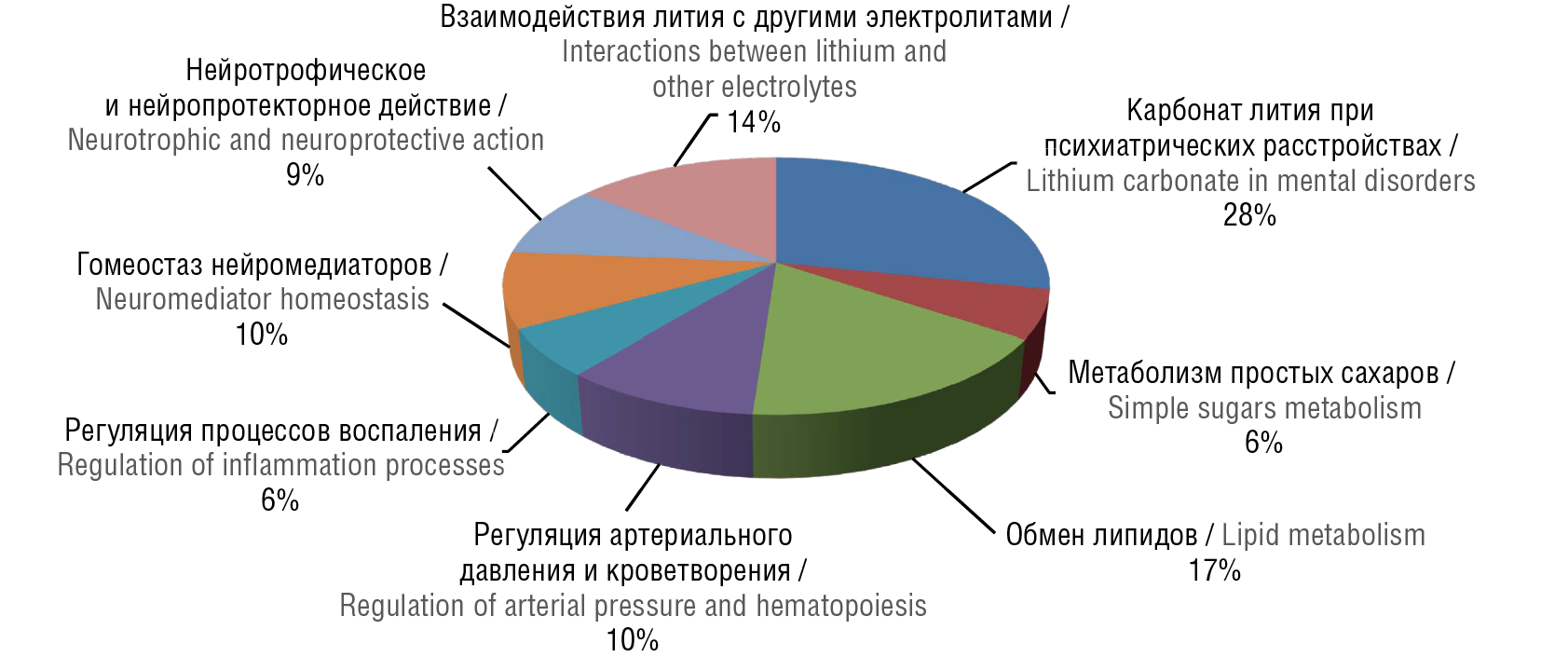
Results. Classification and systematization of all currently available publications on lithium biology and medicine were performed. It was shown that pharmacological applications of lithium salts in mental disorders as well as lithium effects on simple sugars metabolism, lipid metabolism, blood pressure regulation, hematopoiesis, inflammation and tumor growth inhibition, neurotransmitter homeostasis, neurotrophic and neuroprotective molecular mechanisms as well as homeostasis of other electrolytes comprised promising fields of lithium drug research. The prospects for using organic lithium salts, particularly LiAsc, for various therapeutic goals were also discussed. 180-day-long oral administration of LiAsc at doses of 5, 50, 150 mg/kg resulted in no macroscopic signs of local inflammatory reaction while examining its local irritant effect.
Conclusion. The lithium-ion effect on neurotransmitters promotes neuroprotection and reduces a risk of addiction. The antihypertensive, antiatherosclerotic, antidiabetic, antitumor and neurotrophic effects related to organic lithium salts may be beneficial in various therapeutic applications.
EEG РRACTICAL AND TECHNICAL ASPECTS
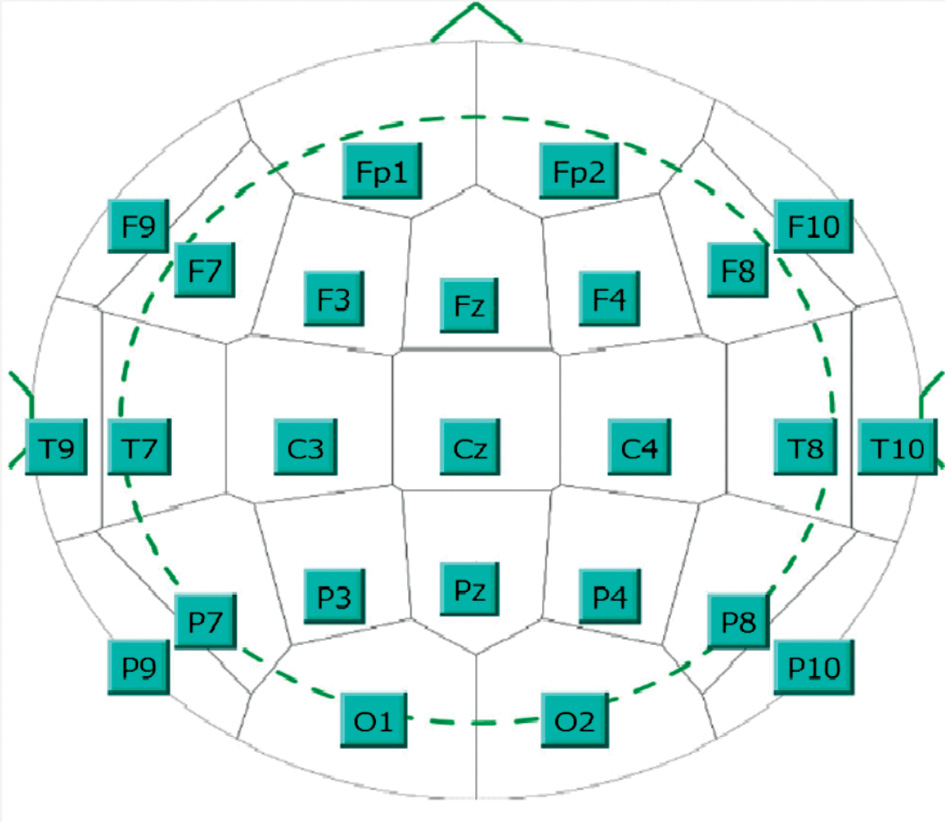
In 2023, the International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology (IFCN) and the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) published the most up-to-date recommendations for conducting EEG examinations. The document sets out minimum standards necessary to improve the accuracy, efficiency, and reliability of routine and sleep EEG recordings. At the same time, it is indicated that based on availability specific rules and methods for conducting examinations should be proposed by medical organizations or departments independently. We present a selective translation of such recommendations and an assessment of their compliance with contemporary real-world opportunities in the Russian Federation. The possible “growth points” for the EEG technique in Russia are highlighted as well.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
ISSN 2311-4088 (Online)